“Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. announced today that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Dupixent® (dupilumab) Injection, the first and only biologic medicine approved for the treatment of adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies, or when those therapies are not advisable.”
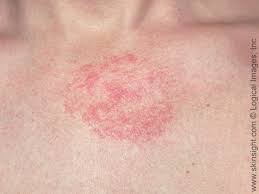
After much anticipation, dupilumab becomes the first biologic approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (a form of eczema). Dupilumab is indicated for adults with moderate to severe eczema that are not well controlled with steroid creams or ointments. The current options for these patients are limited. Most often oral immunosuppressants, like prednisone or cyclosporine, are used. These medications may have several adverse effects. Dupilumab is a biologic that aims to more specifically target the underlying factors driving allergic inflammation. In this case it blocks the signals of two molecules, Il-4 and IL-13.
Approval was based on three studies. The results of these studies showed the medication to be effective for the majority of patients. Additionally, 36-38% of patients achieved clear to almost clear skin.
Dupilumab will come in a pre-filled syringe for self-administration, to be given by subcutaneous injection every other week. A loading dose in your physician’s office may be required.
The wholesale cost was reported $37,000 per year. However, the actual cost to patients is still unknown.
Future directions. Two studies are currently testing safety and effectiveness in children, 6 months to 11 years and 12 to 17 years of age. Other uses under investigation include asthma, nasal polyps and eosinophilic esophagitis.
If you do have atopic dermatitis that is not well controlled, speak to your allergy doctor to see if dupilumab is right for you.
To read more about dupilumab, click here. Also, to read about nemolizumab, a new and similar treatment option, click here.